How to Achieve Personal Growth
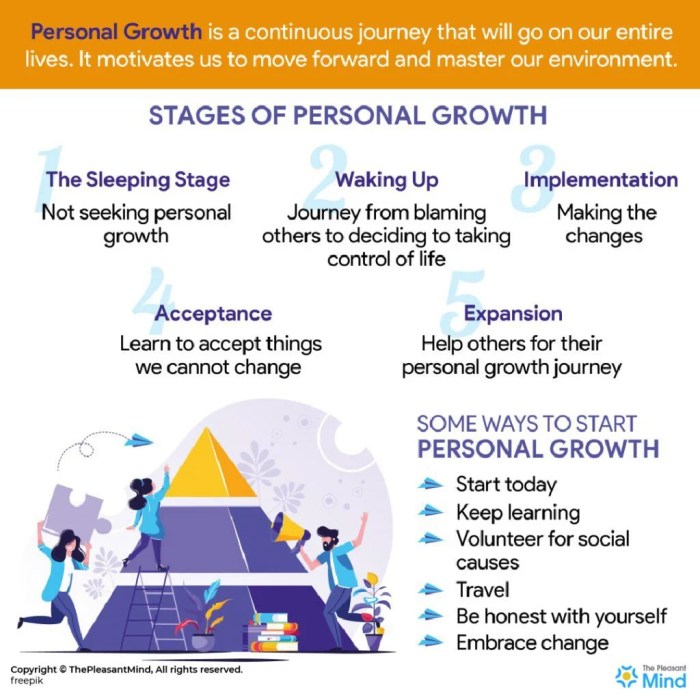
How to achieve personal growth is a journey of self-discovery and transformation. This exploration delves into the multifaceted nature of personal growth, examining its impact on various aspects of life, from career success to fulfilling relationships and robust health. We’ll equip you with practical strategies for setting meaningful goals, navigating obstacles, and cultivating positive habits that foster lasting well-being.
The path to personal growth is paved with self-awareness, resilience, and a commitment to continuous learning. We’ll explore techniques for managing stress and anxiety, building resilience, and utilizing mindfulness practices to enhance mental and emotional well-being. This comprehensive guide provides actionable steps and valuable resources to empower you on your personal growth journey.
Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness, the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment, is a powerful tool for personal growth. It cultivates self-awareness, reduces stress, and fosters emotional regulation, ultimately leading to a more fulfilling and balanced life. This section explores various mindfulness techniques, provides guided meditations for beginners, and discusses how to integrate mindfulness into daily routines.
Different Mindfulness Techniques and Their Benefits, How to achieve personal growth
Several techniques facilitate the cultivation of mindfulness. Mindful breathing, for instance, involves focusing solely on the sensation of breath entering and leaving the body. This simple practice anchors the mind in the present, reducing racing thoughts and promoting relaxation. Body scan meditation involves systematically bringing awareness to different parts of the body, noticing sensations without judgment. This enhances body awareness and can alleviate physical tension.
Mindful walking integrates mindfulness into a common activity, focusing on the physical sensations of walking – the feeling of feet on the ground, the movement of the body. This practice can ground you in the present and reduce stress during daily routines. Each technique offers unique benefits, contributing to improved mental clarity, emotional regulation, and overall well-being.
Guided Meditation Scripts for Beginners
Guided meditations provide a structured approach to mindfulness practice, particularly beneficial for beginners. Here are two examples:
Guided Meditation 1: Mindful Breathing (5 minutes)
Find a comfortable seated or lying position. Close your eyes gently. Bring your attention to your breath. Notice the sensation of the air entering your nostrils, filling your lungs, and leaving your body. If your mind wanders, gently redirect your attention back to your breath. Continue this for five minutes, observing your breath without judgment. When finished, slowly open your eyes.
Guided Meditation 2: Body Scan (10 minutes)
Find a comfortable position. Close your eyes. Bring your attention to your toes, noticing any sensations – tingling, warmth, pressure. Slowly move your awareness up your body, focusing on each part – feet, ankles, calves, knees, and so on, all the way to the top of your head. Notice any sensations without judgment. If you feel tension, simply acknowledge it and let it be. Continue this process for ten minutes. When finished, slowly open your eyes.
Integrating Mindfulness into Daily Life
Integrating mindfulness into daily life doesn’t require extensive time commitments; small, consistent practices are key. Mindful eating, for example, involves paying attention to the taste, texture, and smell of food, savoring each bite without distraction. Mindful listening involves giving your full attention to the speaker, avoiding interruptions or internal distractions. Practicing mindful moments throughout the day – pausing to appreciate a beautiful sunset, or focusing on the sensation of washing your hands – can significantly enhance your overall sense of presence and well-being.
Impact of Mindfulness on Mental and Emotional Well-being
Research indicates a strong correlation between mindfulness practices and improved mental and emotional well-being. Mindfulness reduces stress and anxiety by shifting focus away from rumination and worry. It promotes emotional regulation by increasing self-awareness and acceptance of emotions, preventing emotional overwhelm. Studies have also shown mindfulness to improve sleep quality, reduce symptoms of depression, and enhance cognitive function.
By cultivating a present-moment awareness, mindfulness fosters resilience, enabling individuals to navigate challenges with greater ease and composure.
Mental Health Advocacy
Mental health advocacy plays a crucial role in creating a society that supports and prioritizes the well-being of all individuals. It involves actively working to reduce stigma, increase access to care, and promote policies that protect and enhance mental health. By advocating for better mental health, we build a more compassionate and inclusive community for everyone.Promoting mental health awareness requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the root causes of stigma and promotes understanding.
Effective advocacy can lead to significant improvements in the lives of those affected by mental illness, fostering a culture of support and acceptance.
Promoting Mental Health Awareness in the Community
Raising awareness in your community can involve various strategies, from organizing events to engaging in public education. Effective methods often combine direct engagement with community members alongside strategic partnerships with local organizations. For example, partnering with schools to implement mental health education programs for students and staff can have a significant impact. Collaborating with local businesses to provide employee support programs or mental health resources also increases accessibility.
Public awareness campaigns using social media, local newspapers, or community events can broaden the reach of mental health messages.
Resources for Mental Health Advocacy
Numerous organizations offer support and resources for individuals interested in mental health advocacy. The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provides education, support, and advocacy for individuals and families affected by mental illness. The Mental Health America (MHA) offers similar resources, including educational materials and advocacy tools. Local chapters of these organizations, along with other community-based mental health groups, often provide opportunities for direct involvement in advocacy initiatives.
These groups frequently offer training programs and workshops to equip individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary for effective advocacy. Online resources such as the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) website offer valuable information and tools for individuals seeking to learn more about mental health advocacy.
Combating Stigma Surrounding Mental Health
Stigma surrounding mental health is a significant barrier to accessing care and support. Combating this stigma requires a concerted effort to challenge negative stereotypes and promote understanding. Open and honest conversations about mental health are crucial in normalizing these experiences. Sharing personal stories, when comfortable, can be particularly powerful in reducing stigma and fostering empathy. Educational campaigns designed to dispel myths and misconceptions about mental illness can also help to shift societal attitudes.
Supporting individuals who are open about their mental health challenges and actively challenging discriminatory language and behaviors are further ways to combat stigma. Promoting positive representations of mental health in media and popular culture also plays a significant role in fostering a more accepting society.
Therapy and Counseling Options
Seeking professional help for mental health concerns is a significant step towards personal growth and well-being. Therapy and counseling offer structured support and evidence-based techniques to address a wide range of emotional, psychological, and behavioral challenges. Understanding the different approaches available can help individuals find the best fit for their needs.Therapy and counseling approaches are diverse, each with its own theoretical framework and methods.
The choice of approach often depends on the individual’s specific needs, preferences, and the nature of their concerns.
Types of Therapy and Counseling
Various therapeutic approaches exist, each employing different techniques and focusing on various aspects of mental well-being. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), for example, helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. Psychodynamic therapy explores unconscious patterns and past experiences to understand current difficulties. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) focuses on accepting difficult thoughts and feelings while committing to valued actions.
Other approaches include Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), often used for borderline personality disorder, and mindfulness-based therapies, which emphasize present moment awareness. The effectiveness of each approach varies depending on the individual and their specific condition.
Benefits of Seeking Professional Help
Professional help offers several key benefits. Therapists provide a safe and confidential space to explore personal challenges without judgment. They offer evidence-based strategies to manage symptoms, improve coping mechanisms, and foster personal growth. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from escalating into more significant problems. Moreover, therapy can enhance self-awareness, improve relationships, and promote overall well-being.
For example, someone struggling with anxiety might learn relaxation techniques and cognitive restructuring through CBT, leading to reduced anxiety symptoms and improved quality of life. Similarly, individuals grappling with grief or trauma can find solace and support in therapy, processing their emotions and developing healthy coping mechanisms.
Resources for Finding Qualified Therapists and Counselors
Finding a qualified therapist is crucial. Several resources can assist in this process. Psychology Today’s website offers a searchable database of therapists, allowing individuals to filter by location, specialization, and insurance coverage. The American Psychological Association (APA) and other professional organizations provide directories of licensed psychologists and therapists. Primary care physicians can also offer referrals to mental health professionals within their network.
It’s important to verify the therapist’s credentials and licensing before scheduling an appointment.
Finding a Good Fit with a Therapist
The therapeutic relationship is paramount. Finding a therapist with whom one feels comfortable and connected is essential for successful treatment. The initial consultation often serves as an opportunity to assess the therapist’s approach, personality, and whether their style aligns with the individual’s needs and preferences. Factors such as the therapist’s communication style, their approach to treatment, and their overall demeanor should all be considered.
It’s acceptable to meet with several therapists before finding the right fit. Open communication with the therapist about concerns or preferences is also crucial to building a strong therapeutic alliance. A good fit involves feeling understood, respected, and supported throughout the therapeutic process.
Building Resilience

Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity, stress, and trauma. It’s not about avoiding hardship, but rather about adapting and thriving in the face of challenges. Developing resilience is crucial for personal growth, as it allows individuals to navigate life’s inevitable setbacks and emerge stronger and more capable. A resilient individual possesses the mental fortitude to cope with difficult situations, learn from their experiences, and maintain a positive outlook even when facing significant obstacles.Resilience is a multifaceted skill that can be cultivated and strengthened over time.
It’s not an innate trait; rather, it’s a set of behaviors and coping mechanisms that can be learned and practiced. By understanding the components of resilience and actively engaging in strategies to build it, individuals can significantly enhance their ability to navigate life’s challenges and achieve greater personal growth.
Strategies for Building Resilience
Building resilience involves adopting a proactive approach to managing stress and adversity. This includes developing a strong support network, practicing self-care, and actively seeking opportunities for personal growth. Furthermore, it’s about cultivating a mindset that embraces challenges as opportunities for learning and development, rather than viewing them as insurmountable obstacles. The following strategies can be implemented to effectively enhance resilience:
- Cultivate a positive mindset: Practice gratitude, focus on strengths, and challenge negative self-talk. This involves actively reframing negative thoughts and focusing on solutions rather than dwelling on problems.
- Develop strong social connections: Nurture relationships with supportive friends, family, and mentors. A strong social network provides emotional support and practical assistance during difficult times.
- Engage in self-care: Prioritize physical and mental health through regular exercise, healthy eating, sufficient sleep, and relaxation techniques. This builds a foundation of strength to withstand stress.
- Learn stress management techniques: Practice mindfulness, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga to regulate emotions and reduce stress levels. These techniques help manage the physiological impact of stress.
- Set realistic goals and expectations: Avoid overwhelming yourself with too many commitments. Breaking down large tasks into smaller, manageable steps can increase feelings of accomplishment and reduce stress.
- Embrace challenges as opportunities for growth: View setbacks as learning experiences and opportunities for personal development. Analyze mistakes and adapt strategies for future success.
The Role of Self-Compassion in Building Resilience
Self-compassion involves treating oneself with kindness, understanding, and acceptance, particularly during times of difficulty. It’s about recognizing that everyone makes mistakes and experiences setbacks, and that these experiences are a normal part of life. Self-compassion acts as a buffer against the negative self-judgment and criticism that can exacerbate stress and hinder resilience. By practicing self-compassion, individuals can develop a more positive and supportive inner dialogue, which strengthens their ability to cope with adversity.
For example, instead of berating oneself after a failure, a self-compassionate response might involve acknowledging the difficulty of the situation, recognizing shared human experience, and offering oneself encouragement and support.
Developing Coping Mechanisms for Difficult Situations
Effective coping mechanisms are essential for navigating challenging circumstances. These mechanisms help regulate emotions, manage stress, and maintain a sense of control during difficult times. Developing a range of coping strategies is crucial, as different techniques may be more effective in different situations. Some examples include problem-solving strategies (identifying the problem, brainstorming solutions, and implementing a plan), emotional regulation techniques (mindfulness, journaling, or talking to a trusted friend), and behavioral coping mechanisms (exercise, engaging in hobbies, or spending time in nature).
The key is to identify what works best for each individual and to develop a repertoire of coping skills to draw upon when needed. For instance, someone might find that exercise helps them manage stress, while another might find solace in creative pursuits. Experimentation and self-awareness are key to finding effective coping strategies.
Sleep and Mental Health
Sleep and mental health are intricately linked, forming a bidirectional relationship. Sufficient sleep is crucial for maintaining good mental well-being, while poor sleep significantly impacts mental health, often exacerbating existing conditions or contributing to the development of new ones. Understanding this connection is vital for prioritizing sleep as a key component of overall well-being.Sleep deprivation affects various aspects of mental health.
It impairs cognitive function, leading to difficulties with concentration, memory, and decision-making. Furthermore, it can negatively influence mood regulation, increasing irritability, anxiety, and the risk of experiencing depressive symptoms. The impact extends to emotional processing, making it harder to manage stress and cope with emotional challenges.
The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Mental Well-being
Chronic sleep deprivation weakens the brain’s ability to regulate emotions and cope with stress. This can manifest as increased sensitivity to negative stimuli, heightened emotional reactivity, and difficulty controlling impulsive behaviors. Studies have shown a strong correlation between insufficient sleep and an increased risk of developing or worsening conditions like anxiety disorders, depression, and bipolar disorder. For example, individuals with insomnia are significantly more likely to experience symptoms of depression and anxiety compared to those who sleep soundly.
The lack of restorative sleep disrupts the brain’s natural repair processes, impacting neurotransmitter balance and overall brain function, thus contributing to mental health challenges. The cumulative effect of prolonged sleep deprivation can be substantial, leading to a decline in overall mental health and quality of life.
Tips for Improving Sleep Hygiene
Establishing and maintaining good sleep hygiene is essential for promoting better mental health. This involves creating a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment, and engaging in relaxing bedtime routines. Limiting screen time before bed is crucial, as the blue light emitted from electronic devices interferes with melatonin production, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime are also important factors to consider. A consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, helps regulate the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up feeling refreshed. Incorporating relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises or meditation before bed can further promote sleep quality.
Resources for Individuals Experiencing Sleep Problems
Numerous resources are available for individuals struggling with sleep problems. These include cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), a highly effective treatment that addresses underlying thoughts and behaviors contributing to sleep difficulties. Many mental health professionals offer CBT-I, and online resources and self-help programs are also available. Furthermore, over-the-counter sleep aids, such as melatonin supplements, may provide temporary relief for mild sleep disturbances; however, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before using them, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
Support groups and online communities offer a platform for sharing experiences and finding emotional support from others facing similar challenges. Seeking professional help from a sleep specialist or a physician is advisable for persistent or severe sleep problems, as underlying medical conditions might be contributing to the issue.
Workplace Mental Health: How To Achieve Personal Growth

Prioritizing workplace mental health is crucial for fostering a productive, engaged, and healthy workforce. A supportive and understanding work environment significantly impacts employee well-being, productivity, and overall organizational success. Neglecting mental health in the workplace can lead to decreased morale, increased absenteeism, higher turnover rates, and ultimately, reduced profitability.Workplace stress is a significant contributor to poor mental health. The demands of modern work, including long hours, high pressure, and constant connectivity, can take a toll on employees’ mental well-being.
This stress can manifest in various ways, from mild anxiety and irritability to more serious conditions like depression and burnout. Understanding the impact of workplace stress and implementing strategies to mitigate it is vital for creating a healthier and more sustainable work environment.
Strategies for Promoting Mental Well-being in the Workplace
Implementing comprehensive strategies to support employee mental health is essential. This includes creating a culture of open communication, where employees feel comfortable discussing their mental health concerns without fear of judgment or repercussions. Providing access to mental health resources, such as Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) and mental health professionals, is equally important. Furthermore, promoting work-life balance through flexible work arrangements, reasonable workloads, and encouraging the use of vacation time contributes significantly to employee well-being.
Finally, offering wellness programs, such as mindfulness training or stress management workshops, can equip employees with practical tools to manage their mental health effectively.
Resources for Employers and Employees
Numerous resources are available to support both employers and employees in addressing workplace mental health. For employers, organizations like the Mental Health America (MHA) and the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) offer guidance and resources on creating mentally healthy workplaces. These resources often include best practice guidelines, training materials, and tools for assessing and improving workplace mental health.
Employees can access support through their employer’s EAP, if available, or seek help from independent mental health professionals. Many online platforms and apps offer mental health support, including self-help resources, guided meditations, and access to therapists. The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) provides valuable information and support for individuals and families affected by mental illness.
Impact of Workplace Stress on Mental Health
The detrimental impact of workplace stress on mental health is well-documented. Chronic stress can lead to a range of mental health problems, including anxiety disorders, depression, burnout, and even post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in some cases. The symptoms of stress-related mental health issues can include persistent fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, sleep disturbances, changes in appetite, and feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness.
Prolonged exposure to workplace stress can also weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to physical illnesses. For example, a study published in the journal “Occupational and Environmental Medicine” found a strong correlation between high job strain and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The long-term consequences of unmanaged workplace stress can be severe, affecting both an individual’s personal life and their professional career.
Overcoming Addictions
Addiction is a complex condition that significantly hinders personal growth. It involves a compulsive dependence on a substance or behavior, despite negative consequences. This dependence affects various aspects of life, from physical and mental health to relationships and career prospects. Understanding the different types of addiction and the recovery process is crucial for individuals seeking to reclaim their lives and achieve personal fulfillment.
Types of Addiction and Their Impact
Addictions manifest in diverse forms, impacting personal growth differently depending on the nature of the dependence. Substance use disorders, involving drugs like opioids, stimulants, or alcohol, often lead to physical health problems, financial instability, and damaged relationships. Behavioral addictions, such as gambling, internet addiction, or compulsive shopping, can result in significant debt, social isolation, and feelings of shame and guilt.
All forms of addiction create a cycle of seeking the substance or behavior for temporary relief, which ultimately worsens the underlying issues and prevents personal growth. For instance, someone addicted to gambling might neglect their family and career, sacrificing long-term well-being for the fleeting thrill of the game. Similarly, someone struggling with alcohol addiction may experience liver damage, job loss, and strained relationships, all of which impede their personal and professional development.
Resources for Addiction Treatment
Numerous resources exist to support individuals seeking help for addiction. These include:
- Rehabilitation centers: These facilities provide intensive treatment programs encompassing detoxification, therapy, and support groups.
- Support groups: Organizations like Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and Narcotics Anonymous (NA) offer peer support and guidance.
- Therapy and counseling: Individual and group therapy can help individuals address underlying emotional issues contributing to their addiction.
- Medical professionals: Doctors and psychiatrists can prescribe medication to manage withdrawal symptoms and co-occurring mental health conditions.
- Online resources: Websites and helplines offer information, support, and referrals.
Finding the right resources often involves a process of trial and error. It’s essential to seek professional guidance to determine the most appropriate course of action based on individual needs and circumstances.
The Recovery Process from Addiction
Recovery is a journey, not a destination, often characterized by setbacks and relapses. It typically involves several key stages:
- Admission and acceptance: Acknowledging the problem and accepting the need for help is the crucial first step.
- Detoxification: This process, often medically supervised, involves safely withdrawing from the substance or behavior.
- Therapy and counseling: Addressing underlying emotional issues, developing coping mechanisms, and learning relapse prevention strategies are critical.
- Lifestyle changes: Adopting healthy habits, building a strong support system, and engaging in activities that promote well-being are essential for long-term recovery.
- Ongoing support: Continued participation in support groups, therapy, and self-care practices is vital for maintaining sobriety and preventing relapse.
The recovery process is unique to each individual and may require adjustments along the way. Consistent effort, self-compassion, and a strong support system are key factors in successful recovery.
Strategies for Preventing Relapse
Relapse is a common occurrence in addiction recovery, but it doesn’t signify failure. Strategies to minimize the risk of relapse include:
- Identifying triggers: Recognizing situations, people, or emotions that increase the urge to use is crucial for developing coping mechanisms.
- Developing coping mechanisms: Learning healthy ways to manage stress, cravings, and negative emotions is essential.
- Building a strong support system: Surrounding oneself with supportive friends, family, and professionals can provide encouragement and accountability.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Prioritizing physical and mental health through exercise, nutrition, and mindfulness practices can improve overall well-being and reduce vulnerability to relapse.
- Seeking professional help immediately: If cravings or urges become overwhelming, seeking help from a therapist, sponsor, or medical professional is crucial.
Consistent self-monitoring and proactive planning are vital in preventing relapse.
Personal Growth and Self-Care
Personal growth and self-care are intrinsically linked; one cannot truly flourish without the other. Self-care isn’t selfish indulgence; it’s the essential foundation upon which personal growth is built. By prioritizing our well-being, we cultivate the resilience, energy, and clarity necessary to pursue our goals and overcome challenges. Neglecting self-care, on the other hand, can lead to burnout, decreased motivation, and hinder our ability to achieve personal development.Self-care encompasses a wide range of practices designed to nurture our physical, mental, and emotional health.
These practices are not one-size-fits-all; finding what works best for you is key to making self-care a sustainable part of your life. The effectiveness of self-care stems from its ability to reduce stress, improve mood, and increase overall energy levels, all crucial components of successful personal growth.
Types of Self-Care Practices
Self-care activities can be broadly categorized into physical, mental, and emotional practices. Physical self-care focuses on maintaining a healthy body through proper nutrition, exercise, and sufficient sleep. Mental self-care involves activities that stimulate the mind and promote cognitive well-being, such as reading, learning new skills, or engaging in creative pursuits. Emotional self-care centers on managing and processing emotions through techniques like journaling, meditation, or spending time in nature.
A balanced approach incorporating all three aspects is most effective.
Prioritizing Self-Care
Prioritizing self-care is not a luxury but a necessity for sustained personal growth. It requires conscious effort and intentionality. Scheduling dedicated time for self-care, much like any other important appointment, is crucial. This could involve setting aside 30 minutes each morning for meditation or an hour each week for a relaxing hobby. It’s also important to be flexible and adapt your self-care routine to accommodate life’s inevitable changes.
Consistency, however, is key to reaping the benefits. Remember that neglecting self-care can lead to decreased productivity, increased stress, and ultimately, hinder your personal growth journey.
Self-Care’s Contribution to Well-being and Personal Growth
Self-care directly contributes to overall well-being and fuels personal growth. By addressing our physical, mental, and emotional needs, we create a supportive environment for personal development. Reduced stress levels lead to clearer thinking and improved decision-making, allowing us to pursue our goals with greater focus and determination. Increased energy levels and improved mood contribute to increased motivation and resilience in the face of adversity.
Self-care fosters self-awareness, helping us identify our strengths and weaknesses, enabling us to make informed choices about our personal growth trajectory. In essence, self-care empowers us to live a more fulfilling and meaningful life.
Examples of Self-Care Activities
It’s important to cultivate a diverse range of self-care activities to address various aspects of well-being. The following list provides a variety of options to consider:
- Exercise regularly
- Prioritize sleep (7-9 hours per night)
- Eat a healthy diet (balanced meals, plenty of fruits and vegetables)
- Engage in hobbies (reading, painting, playing music, etc.)
- Spend time in nature (walking in a park, hiking, gardening)
- Practice mindfulness (meditation, deep breathing exercises)
- Connect with loved ones (spending quality time with family and friends)
- Set boundaries (learning to say no to protect your time and energy)
- Seek professional help when needed (therapy, counseling)
Ultimately, the journey of How to achieve personal growth is a deeply personal one, requiring self-reflection, consistent effort, and a willingness to embrace change. By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide—from setting SMART goals and building positive habits to managing stress and seeking support when needed—you can cultivate a life of greater fulfillment, purpose, and well-being. Remember that progress, not perfection, is the key to sustainable personal growth.
Embrace the process, celebrate your achievements, and never stop learning and evolving.
FAQ Corner
What if I don’t see results immediately?
Personal growth is a marathon, not a sprint. Be patient with yourself and celebrate small victories along the way. Consistent effort over time yields significant results.
How do I know what goals to set?
Reflect on your values, passions, and areas where you want to improve. Consider what truly matters to you and set goals aligned with your authentic self.
What if I experience setbacks?
Setbacks are inevitable. View them as learning opportunities. Analyze what went wrong, adjust your approach, and keep moving forward. Resilience is key.
When should I seek professional help?
If you’re struggling with persistent negative emotions, significant challenges, or feel overwhelmed, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance from a therapist or counselor.



